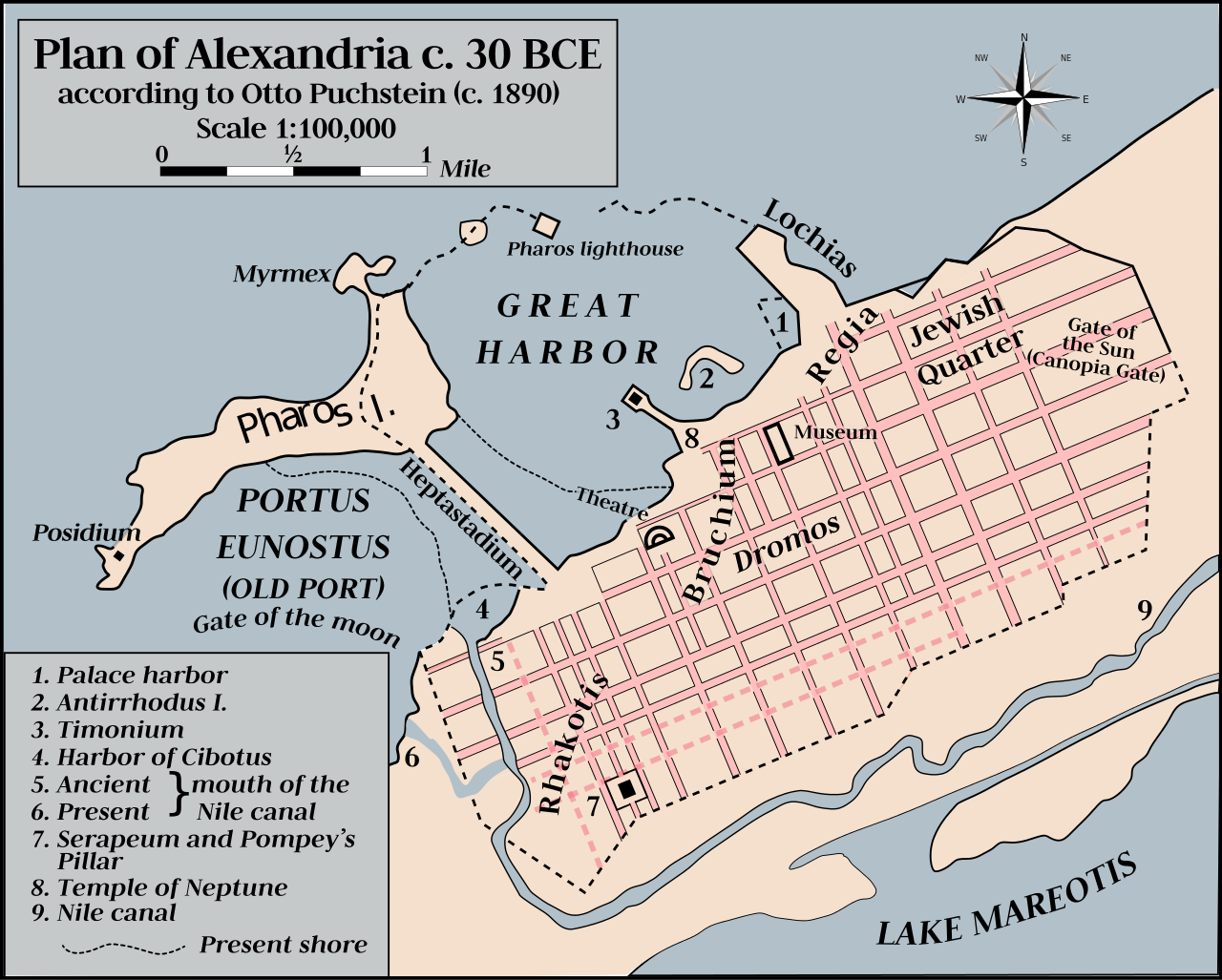
A
map of Alexandria harbour, showing Antirhodos Island, where
Cleopatra's Temple was located before 365AD.
Fourteen
hundred years ago in Egypt there was a terrible earthquake and a huge tsunami that hit the coast of the great city of Alexandria. It sank the island of Antirhodos, taking down queen Cleopatra’s palace and
Alexandria’s old
lighthouse, once a wonder of the ancient world.
All was well on the small island of Antirhodos off the coast of Alexandria. The place was like a cul de sac of temples and monuments from the ancient world.
We imagine that the site is going to become an even more popular destination once the
proposed Cleopatra movie featuring
Gal Gadot hits the screen worldwide.
Or, the biopic starring Zendaya,
also brewing at time of writing, under the capable hands of
Denis Villeneuve.
When Antirhodos was discovered by underwater archaeologists Franck Goddio and Ashraf Abdel Raouf in 1996, it revealed that careful architectural preparation was carried out around 250BC for its subsequent urbanization.
Cleopatra’s palace at Atirhodos existed until the year 365 when a massive earthquake – believed to have been the biggest in the Ancient
Mediterranean, sent off a wave of destruction that reached as far as the shores of
Spain.
The earthquake’s epicentre was off the island of Crete. Nearby Alexandria could not have been spared by the gargantuan tsunami that
leveled the neighborhoods, temples and harbors of this important city.
The Roman soldier Ammianus Marcellinus a witness of the event, describes what happened in grim detail: there had been a terrible tremor followed by the sea rolling back far from human sight, revealing magnificent ravines and valleys underneath. As people were busy gathering stranded creatures on the sea bed, the sea made a roaring return resulting in the death of thousands.
The jewel of the island is, of course, Cleopatra’s now-underwater palace which lies submerged five meters or 16 feet underwater. It is only ironic that, like the site itself, Cleopatra’s final resting place is waiting to be discovered.
Egypt’s last Pharaoh of the Macedonian Ptolemaic dynasty took her own life together with her lover Mark Antony following her kingdom’s defeat to
Rome at the
Battle of
Actium.
Until Egypt builds its planned underwater museum in Alexandria, history buffs and adventurers would have to settle with the feat of seeing Cleopatra’s underwater palace from behind scuba diving gear.
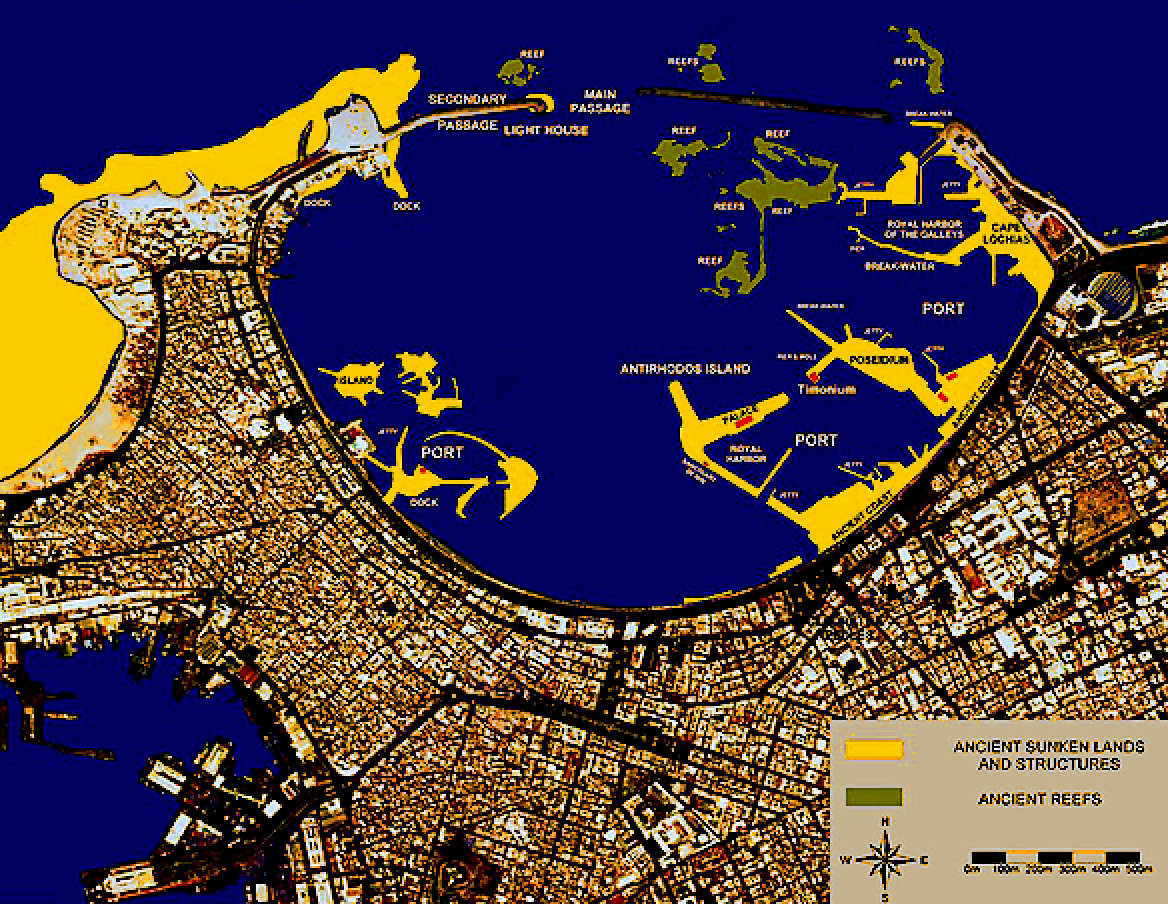
In its current state, the site offers a 30-meter long ship that was wrecked underneath the tsunami along with the goods it carried, 7-meter tall pillars, granite blocks from the different temples, sphinxes, statues, and more.
Cleopatra’s underwater palace is one of the sites where she may have been buried along with Mark Antony. Of the three proposed crypts where her remains may have been interred, the palace of Antirhodos has been least investigated.
This royal-quarter area in the Eastern Harbour has yielded some of Alexandria's most interesting underwater antiquities. Today divers can see a couple of large, enigmatic
sphinxes as well as red-granite columns, platforms and pavements that archaeologists speculate formed part of a former palace. There's also a remarkably complete shipwreck here that has been carbon-dated to between 90 BC and AD 130. Depth: 5m. Rating: novice. Dives can be arranged through Alexandra Dive.
As many readers will know Cleopatra’s palace featured in the 4th
Tomb Raider game known as “The Last Revelation” Found in level 20,
when the palace took on a different feel and aesthetic.
However, it was not only being a students of Egyptology that attracted
us to this theme. It was also the sunken city aspect of it all.
Many will know that the legend of Kitezh that encompasses Rise of the
Tomb Raider was also about a sunken
city. And one of the Lara
Croft movies also features a sunken city.
We
thus discuss the similarity reaching across the years of the franchise and bridging the gap between old and new. By this
we mean, the actual palace of Cleopatra VII was located on an island that later
sank.
HISTORY
After
Alexander the Great conquered Egypt in 332
BC, he founded Alexandria.
For nearly a millennium, Alexandria was the Mediterranean’s bustling
port, with Antirhodos Island inside the harbour. Then Alexandria
was washed into the Mediterranean Sea in AD 365.
Cleopatra may not have been interned in the Temple
Palace, but the port of Thonis-Heracleion was also sunk
by the same tsunami, along with other close by settlements.
Antirhodos (sometimes Antirrhodos or Anti Rhodes) was in the eastern harbor of
Alexandria, Egypt, on which a
Ptolemaic Egyptian palace was sited. The island was occupied until the reigns of Septimius Severus and Caracalla and it probably sank in the 4th century, when it succumbed to earthquakes and a tsunami following an earthquake in the eastern Mediterranean near Crete in the year 365. The site now lies underwater, near the seafront of modern Alexandria, at a depth of approximately five metres (16 ft).
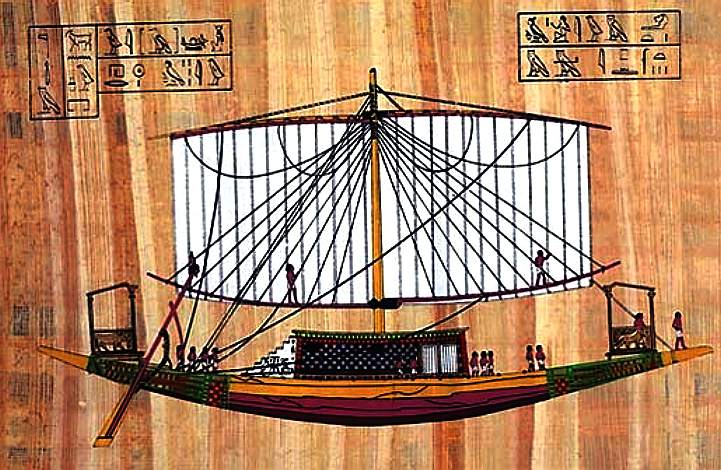
Descriptions of the island were recorded in classical antiquity by Greek geographers and historians. Strabo described a royal house on Antirhodos in 27 BC and wrote that the island's name ("counter-Rhodes") derived from the island's rivalry with the island of Rhodes. Antirhodos was part of Alexandria's ancient royal port called the Portus Magnus, which also included parts of the Lochias peninsula in the East and the island of Pharos in the West. The Portus Magnus was abandoned and left as an open bay after an earthquake in the 8th century.

REDISCOVERY
In 1996, underwater archaeology in the harbour of Alexandria conducted by
Franck Goddio located the island and found that it was on the opposite side of the harbour from where it was placed by Strabo. The excavations showed that the island had been occupied from before the founding of Alexandria and that it was totally levelled and prepared for construction around 250BC.
The island was small (about 500 hectares or 1,200 acres) and fully paved, with three branches leading in different directions. The main branch was 300 metres (1,000 ft) long and had an esplanade facing the site of the
Caesarium temple on the mainland seafront.
On the esplanade Goddio uncovered the remains of a relatively modest (90 metres by 30 metres) marble-floored 3rd century BC palace, believed to have been
Cleopatra's royal quarters. On another narrow branch of the island there was a small Temple of Isis which had at its entrance a life-size granite statue representing a shaven-headed Egyptian priest of the goddess Isis carrying a jar topped with an image of
Osiris. A pair of granite sphinxes flanked the statue, one of which had the head of Cleopatra's father.
Between the branches on the eastern side of the island there was a small port with docks. Here there was a series of 60 columns, each 1 metre in diameter and 7 metres in length, made of red Egyptian granite and topped with a decorated crown. Ancient paintings indicate that the columns acted as the ceremonial gateway to the island. The wreck of a 30-metre long 1st century BC or 1st century AD Roman ship has been identified in the vicinity of the port. Evidence from a hole in the ship's hull suggests that it could have sunk after being rammed by another boat.
The site of Mark
Antony's uncompleted palace, the Timonium, has also been located on the island. Other finds include a colossal stone head thought to be of Cleopatra's son Caesarion, and a huge quartzite block with an engraving of a pharaoh and an inscription indicating that it depicts Seti I, father of
Ramses
II. Some of the pharaonic objects on the site had been brought from Heliopolis by the
Ptolemaic rulers and re-used to construct their buildings. The remains on the island do not seem to date from later than the Ptolemaic period, suggesting the palace may have been abandoned soon after Cleopatra's death and the absorption of Egypt into the Roman Republic.
The
abandonment also suggests that Cleopatra was not entombed in
the palace, but elsewhere.
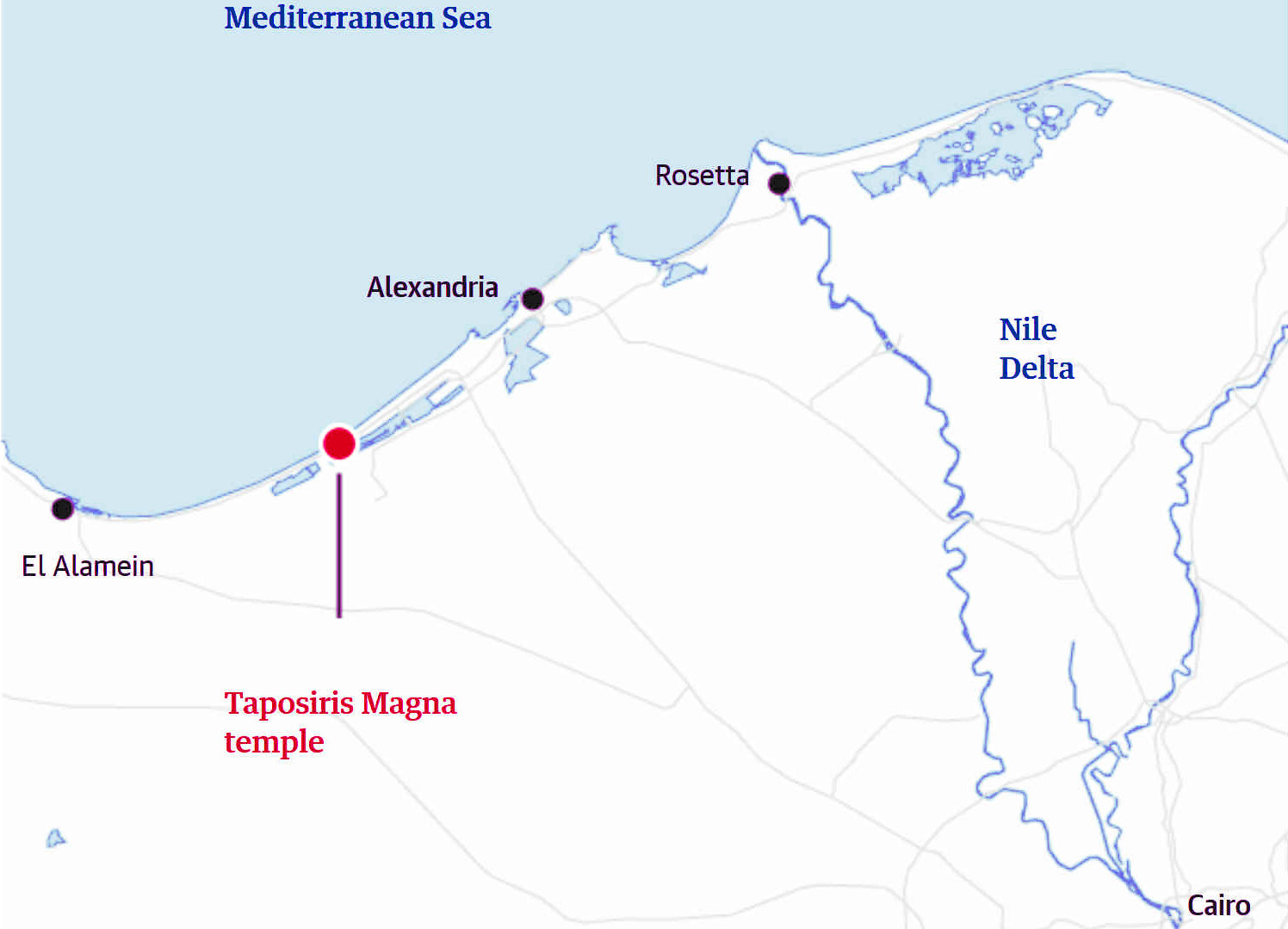
The search for
Cleopatra's elusive tomb, has been at various locations
along the Egyptian coast, including Taposiris Magna.
Perhaps most significant, he has found that much of ancient Alexandria sank beneath the waves and remains remarkably intact. Using sophisticated sonar instruments and global positioning equipment, and working with scuba divers, Goddio has discerned the outline of the old port’s shoreline.
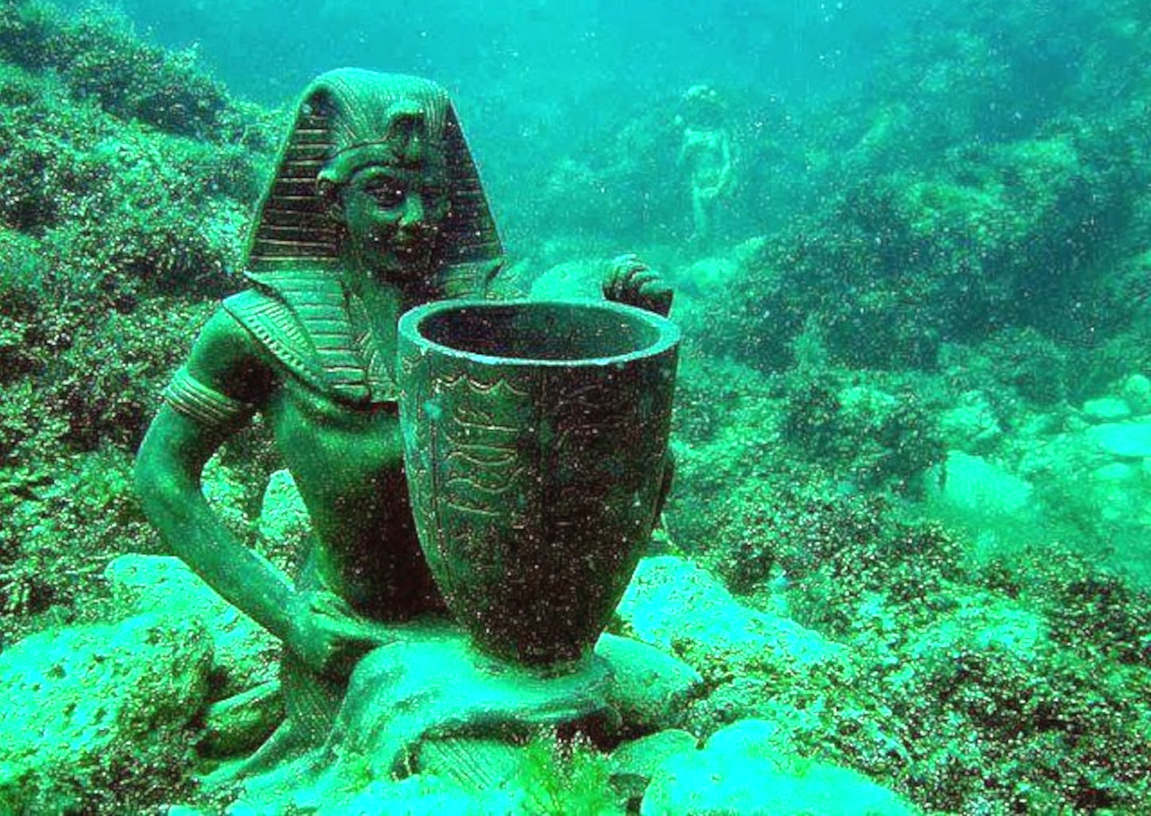

On August 21, in A.D. 365, the sea suddenly drained out of the harbor, ships keeled over, fish flopped in the sand. Townspeople wandered into the weirdly emptied space. Then, a massive
tsunami surged into the city, flinging water and ships over the tops of Alexandria’s houses, according to a contemporaneous description by Ammianus Marcellinus based on eyewitness accounts. That disaster, which may have killed 50,000 people in Alexandria alone, ushered in a two-century period of seismic activity and rising sea levels that radically altered the Egyptian coastline.
REFERENCE
https://www.uwphotographyguide.com/diving-cleopatras-palace

The
Mediterranean Sea is awash with sunken treasures. When Alexander
the Great died in Babylon in 323 BC, his companion, Ptolemy I, laid claim to Egypt as his domain. He founded a dynasty that was to rule for three hundred years from Alexandria. Ptolemy II made Alexandria
the center of culture and founded the Alexandria Library and
Museo, the first research center and “think tank.” The Pharos Lighthouse was built, and it was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Its beam of light could be seen for thirty miles.










