The Ptolemaic Kingdom (Koinē Greek: Πτολεμαϊκὴ βασιλεία, romanized: Ptolemaïkḕ basileía) was an Ancient Greek state based in
Egypt during the Hellenistic Period. It was founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter, a companion of Alexander the Great, and lasted until the death of
Cleopatra VII in 30 BC. Ruling for nearly three centuries, the Ptolemies were the longest and most recent Egyptian dynasty of ancient
origin, with Ptolemy XII producing Cleopatra VII and Arsinoe
IV.
Alexander the Great
conquered Persian-controlled Egypt in 332 BC during his campaigns against the Achaemenid Empire. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, his empire quickly unraveled amid competing claims by the diadochi, his closest friends and companions. Ptolemy, a Macedonian who was one of Alexander's most trusted generals and confidants, won control of Egypt from his rivals and declared himself
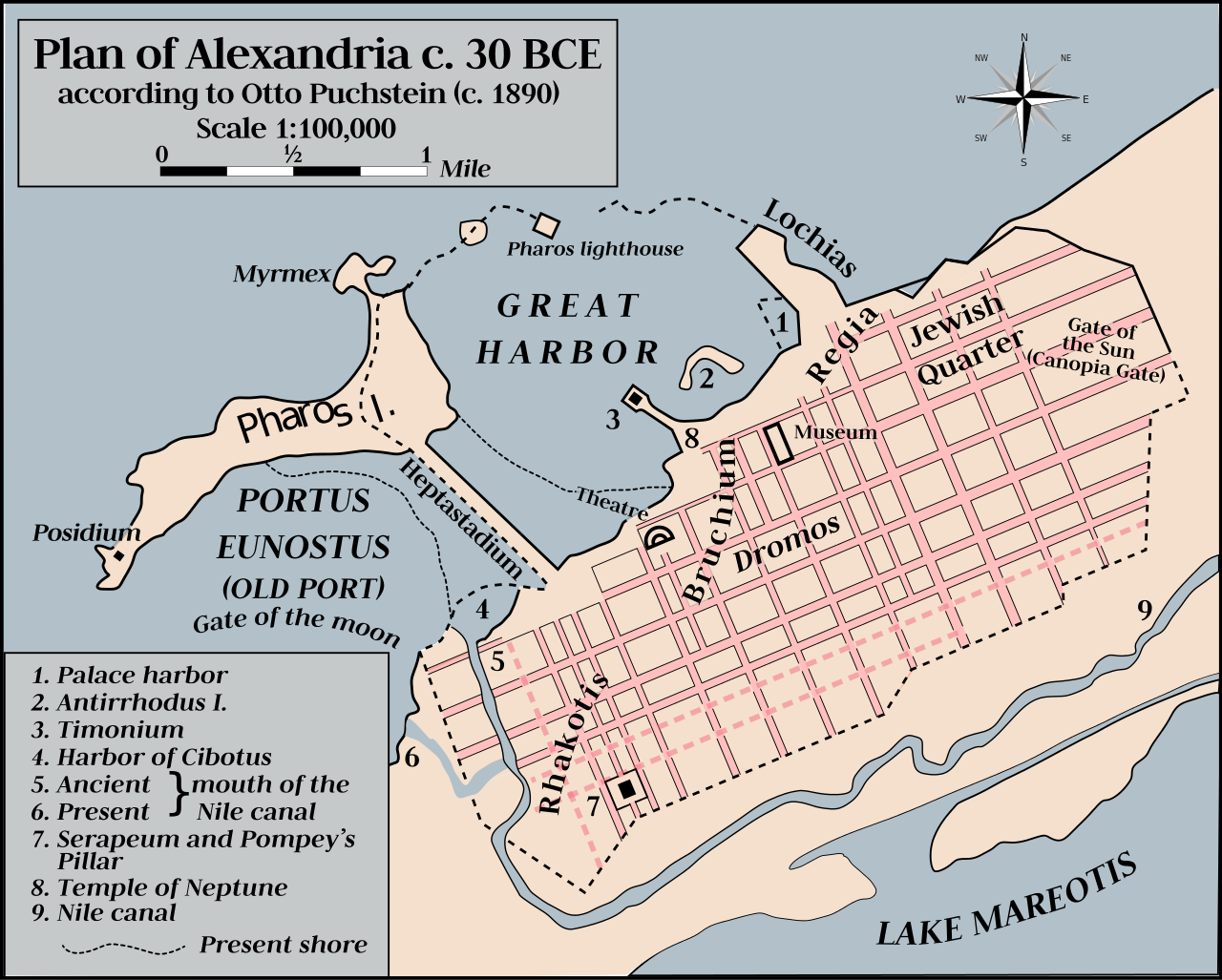
Pharaoh. Alexandria, a Greek polis founded by Alexander, became the capital city and a major center of Greek culture, learning, and trade for the next several
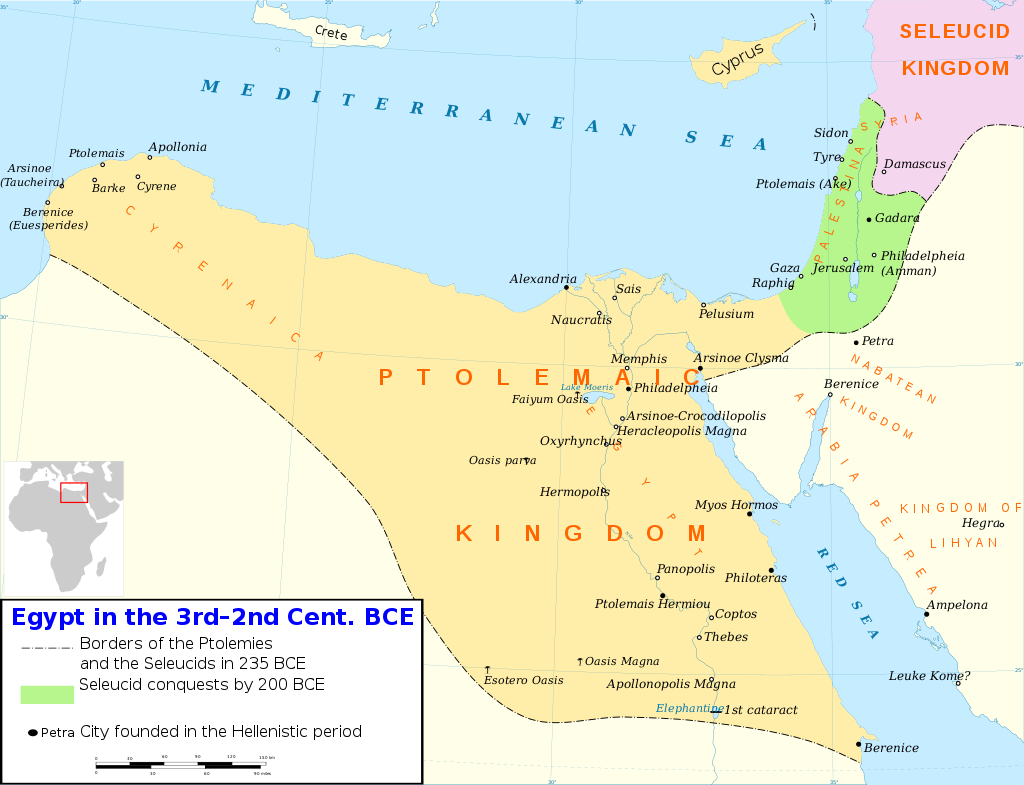
centuries. Following the Syrian Wars with the Seleucid Empire, a rival
Hellenistic state, the Ptolemaic Kingdom expanded its territory to include eastern Libya, the Sinai, and northern Nubia.
To legitimize their rule and gain recognition from native Egyptians, the Ptolemies adopted the title of the pharaoh and had themselves portrayed on public monuments in Egyptian style and dress; otherwise, the monarchy rigorously maintained its Hellenistic character and traditions. The kingdom had a complex government bureaucracy that exploited the country's vast economic resources to the benefit of a Greek ruling class, which dominated military, political, and economic affairs, and which rarely integrated into
Egyptian society and culture. Native Egyptians maintained power over local and religious institutions, and only gradually accrued power in the bureaucracy, provided they Hellenized. Beginning with Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the Ptolemies began to adopt Egyptian customs, such as marrying their siblings per the
Osiris myth, and participating in Egyptian religious life. New temples were built, older ones restored, and royal patronage lavished on the priesthood.
From the mid third century BC, Ptolemaic Egypt was the wealthiest and most powerful of Alexander's successor states, and the leading example of Greek civilization. Beginning in the mid second century BC, dynastic strife and a series of foreign wars weakened the kingdom, and it became increasingly reliant on the Roman Republic. Under
Cleopatra
VII, who sought to restore Ptolemaic power, Egypt became entangled in a
Roman civil war, which ultimately led to its conquest by Rome as the last independent Hellenistic state. Roman Egypt became one of Rome's richest provinces and a center of
Macedonian culture, with Greek remaining the main language of government until the Muslim conquest in 641 AD. Alexandria remained one of the leading cities of the
Mediterranean
Sea
well into the late Middle Ages.