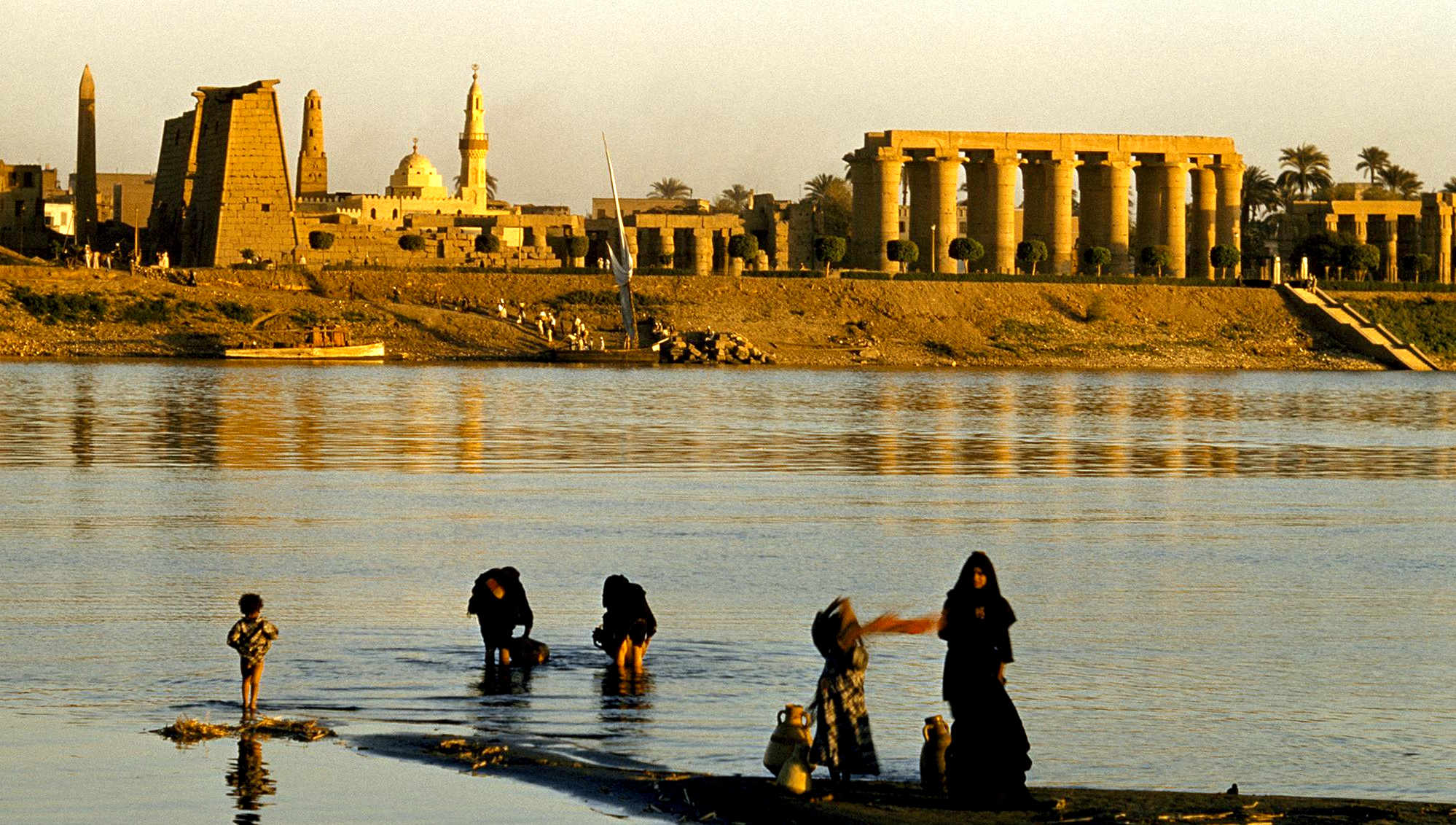

The
River Nile gave life to Egypt
The Battle of the Nile in 47 BC (not to be confused with the Napoleonic
engagement in 1798) saw the combined Roman–Egyptian armies of Julius Caesar and
Cleopatra VII defeat those of the rival
Queen Arsinoe IV and King Ptolemy XIII and secure the throne of
Egypt.
BUILD UP
After pursuing his rival Pompey to Egypt, Caesar, recently victorious in a civil war closer to home, became entwined in the Alexandrine civil war after his rival, Pompey Magnus, was killed by King Ptolemy XIII in an attempt to please Caesar.
From September 48 BC until January 47 BC, Caesar was besieged in Alexandria, Egypt with about 4,000 men. He was attempting to resolve the Egyptian Civil War between Ptolemy XIII and his sister Cleopatra. When Caesar began to appear to favour Cleopatra over him, Ptolemy was first captured, but then released by Caesar, and gathered his army to besiege the Romans in a small area of Alexandria.
By January, the Egyptians had begun to get the upper hand in their efforts to cut the Romans off from reinforcements and resupply. Caesar had requested reinforcements from his allies who gathered an army of about 13,000 troops trained in the Roman style of warfare under Mithridates of Pergamum, who marched overland from Asia Minor to assist him. Arriving in Egypt in January, Mithridates stormed and took the strategic city of Pelusium and marched on towards the
Nile Delta where he defeated an Egyptian force sent to stop him. A Jewish force, led by Antipater, also joined them. Caesar, getting a message that his allies were close, left a small garrison in Alexandria and hurried to meet them. The combined force, about 20,000 strong, met the Egyptians in February 47 BC at the Battle of the Nile. The Ptolemaic army, equipped in the Greek manner, was slightly larger.
THE BATTLE
The Egyptians had set up camp in a strong position along the Nile, and were accompanied by a fleet. Caesar arrived shortly afterwards, before Ptolemy could attack Mithridates' army. Caesar and Mithridates met 7 miles from Ptolemy's position. In order to reach the Egyptian camp they had to ford a small river. Ptolemy sent a detachment of cavalry and light infantry to stop them from crossing the river. Unfortunately for the Egyptians, Caesar had sent his Gallic and Germanic cavalry to ford the
Nile
ahead of the main army. They had crossed the river
undetected. When Caesar arrived he had his men make makeshift bridges across the river and had his army charge the Egyptians. As they did the Gallic and Germanic forces appeared and charged into the Egyptian flank and rear. The Egyptians broke and fled back to Ptolemy's camp, with many fleeing by boat. As Ptolemy himself tried to flee, his ship became overloaded and capsized, killing him.


AFTERMATH
Egypt was now in the hands of Caesar, who then lifted the Siege of Alexandria and placed Cleopatra on the throne as co-ruler with another of her brothers, the twelve-year old Ptolemy XIV. Caesar then uncharacteristically lingered in Egypt until April, enjoying a liaison of about two months with the youthful queen before departing to resume his civil war. Around this time, she became pregnant with Caesarion. The former queen
Arsinoe IV was marched through
Rome as a prisoner and banished to the Temple of Artemis in Ephesus. Later, after the death of Caesar, she was executed on the orders of Cleopatra and Mark Antony.
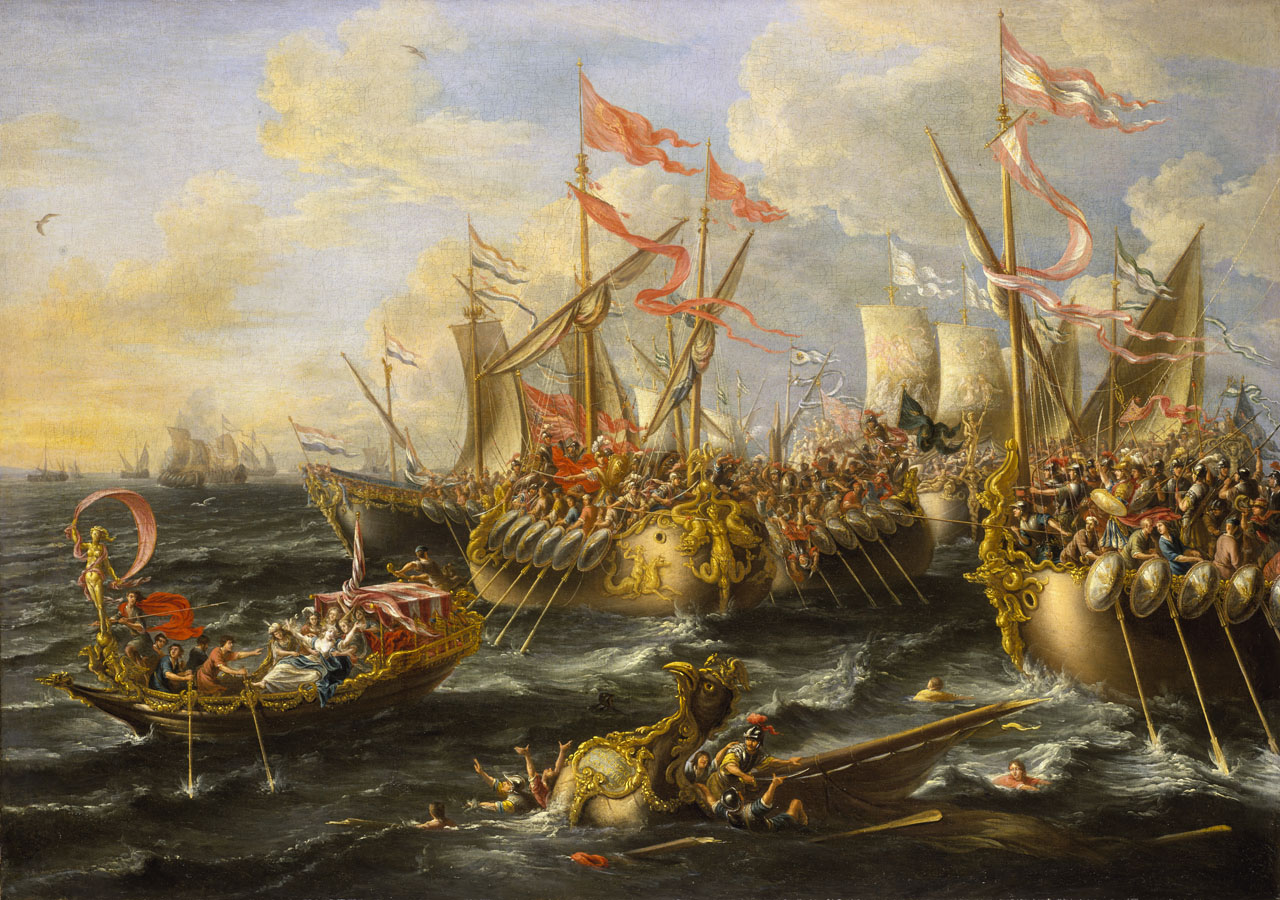

The
Battle of Actium, Ionian Sea - the second decisive naval engagement for
Cleopatra
|
|
Please use our
A-Z to
navigate this site or return HOME

The rights of Jameson Hunter and Cleaner Ocean Foundation to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with section 77 and 78 of the Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988.
This website and the
associated Cleopatra
artwork is Copyright © 2022 Cleaner Ocean Foundation and Jameson Hunter.
This is a work of fiction. Names and characters are the product of the
authors' imaginations, and any resemblance to any person, living or
deceased, is entirely coincidental.
|




